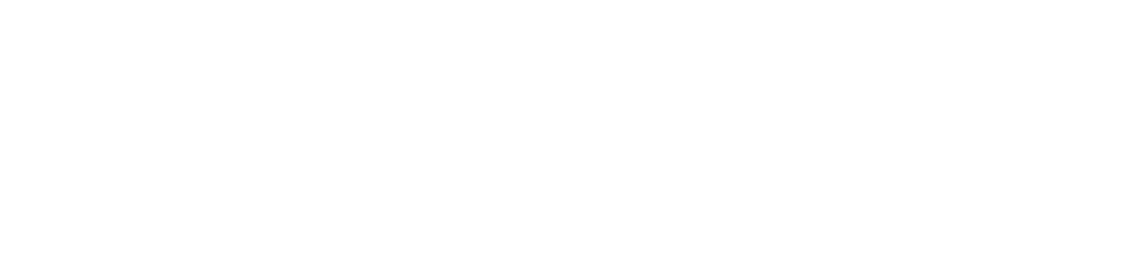What Does a CT Scan Show?
CT scans are often used to check for:
- Abdominal problems
- Heart and blood vessel issues
- Muscle or bone injuries
- Brain and nerve conditions
- Spine problems
- Chest and lung conditions
CT scans are especially good at showing air, blood, and calcium. This makes them very helpful for looking at the lungs and other air-filled areas. Unlike an MRI, a CT scan is done in an open machine shaped like a donut, so you can see around you and won’t feel closed in.
Common Uses of CT
Doctors often order CT scans to:
- Find cancer and see the size, shape, and location of a tumor
- Guide a biopsy by helping place a needle in the right spot
- Plan treatments, including radiation therapy
- Check injuries after an accident
- Look for aneurysms or strokes
How a CT Scan Works
During the test, you will lie on a table that slowly moves through a large ring. As you pass through, the scanner takes many pictures of your body. A computer then builds these into detailed images.
Sometimes, a contrast material is used to make the pictures clearer. This contrast may be given by mouth or through an IV, depending on the type of exam.
Types of CT Scans
Low-Dose CT Lung Cancer Screening
This test helps find lung cancer early, before symptoms appear. It is quick, simple, and does not use needles, dye, or fasting. The machine is donut-shaped, not a tunnel, so there is no feeling of being trapped.
Calcium Scoring
This test looks at your heart to measure calcium in your arteries. The score helps doctors check your risk for heart disease. A lower score means lower risk. Heart disease often has no symptoms, and this scan can give early warning.
CT Angiography (CTA)
CTA is a scan of your blood vessels. It shows blockages or damage in veins and arteries. With contrast dye, it gives doctors a clear view of how blood flows through your body.
How Much Does a CT Scan Cost in Phoenix?
The cost of a CT scan in Arizona depends on a few factors, including the type of CT scan performed, whether contrast dye is used, the area of the body being scanned, and your insurance coverage, co-pay, or deductible.
On average, hospitals can charge up to twice as much for the same exam, often due to higher facility fees and overhead costs.
Many patients choose outpatient imaging centers like Arizona Diagnostic Radiology to get the same high-quality CT scans at a fraction of the price. According to the National Institute for Health Care Reform, community-based imaging centers may charge up to 50% less than hospital outpatient departments for identical procedures (source).
By choosing an outpatient facility, patients can enjoy significant cost savings, shorter wait times, and a more comfortable experience, all without compromising quality or accuracy. Arizona Diagnostic Radiology provides affordable CT scans in Phoenix, using advanced technology and expert radiologists to deliver precise, reliable results you can trust.